Manual Reconciliation vs Automatic Reconciliation: What’s the Difference and When to Use Each

Businesses deal with numbers every day, payments, expenses, refunds, chargebacks, vendor invoices, and more. Eventually, everything has to line up. That’s where Manual and Automatic Reconciliation come in. Both confirm whether financial records match reality, but they work in very different ways and suit different stages of growth. Understanding how each method functions, and where each one performs best, helps teams stay accurate, efficient, and ready to scale.
- Manual Reconciliation vs Automatic Reconciliation: What’s the Difference and When to Use Each
What Makes Manual Reconciliation Different?
Manual Reconciliation is exactly what it sounds like: a person (or a team) goes line by line through transactions, matching internal records to bank statements, platform payouts, vendor invoices, or other data sources. With Manual Reconciliation, someone physically confirms every amount, every reference, and every date.
Because Manual Reconciliation depends on human review, it tends to be slower and more prone to error, but it also allows for deeper scrutiny and context-aware judgement. Teams often apply Manual Reconciliation for exceptions, unusual entries, compliance-heavy tasks, or transactions where context matters more than speed.
Businesses with complex billing or multiple payment channels often begin with Manual Reconciliation to get visibility into where they might have data entry issues, mismatches, or manual-process leaks.
How Automatic Reconciliation Changes the Process
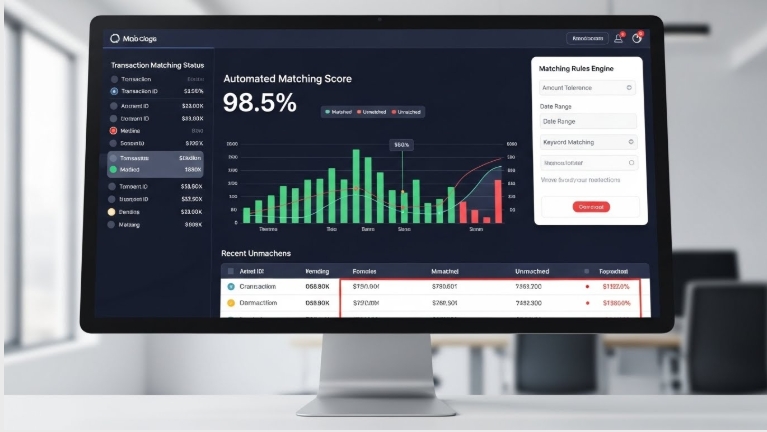
Automatic Reconciliation replaces slow, manual matching with a fast, software-driven process. With tools like Bycard, structured data flows directly from transactions, virtual cards, vendor payments, and receipts into your finance system. The platform pulls information from multiple sources, bank feeds, ledgers, payment gateways, card activity, and vendor reports, and applies smart rules such as amounts, dates, invoice numbers, card IDs, and reference codes to match transactions automatically. Clean matches are reconciled instantly, while irregular items are flagged for human review. Because Bycard attaches metadata to every spend, accuracy improves and exceptions decrease. Some systems even learn from past resolutions, making future reconciliations smoother. The result is a real-time workflow that gives finance teams clearer visibility, faster reporting, and less manual effort.
Manual Reconciliation vs Automatic Reconciliation
1. Speed and Volume
Manual Reconciliation requires reviewing each transaction one by one, which becomes painfully slow as volumes grow. Automatic Reconciliation, on the other hand, processes thousands of lines in minutes by batching and matching data instantly. As businesses scale, especially those pulling data from multiple sources, manual checks quickly become inefficient and error-prone. Automation becomes essential for high-volume or multi-channel operations, while manual methods only remain practical for very low or occasional activity. Automatic Reconciliation lets companies grow without increasing headcount or wasting hours on repetitive reviews.
2. Accuracy and Error Rate
Human error is one of the biggest risks with Manual Reconciliation. Mistyped amounts, missing entries, wrong dates, all of these mistakes can creep in. Spreadsheets, manual imports, and copy‑pasting all amplify risk.
By contrast, Automatic Reconciliation applies the same matching logic consistently, reducing error rates significantly. Well-implemented automated matching algorithms can produce accuracies up to 99.7%, dramatically reducing unmatched transactions and write-off tracking errors.
3. Flexibility and Context
Automation is powerful, but it isn’t perfect, especially when context or judgment is involved.
With Manual Reconciliation, humans can handle edge cases: ambiguous vendor names, missing reference codes, delayed settlements, refunds processed outside standard channels, or intercompany adjustments. A person can interpret context, ask follow-up questions, and apply discretion, something an algorithm may mis-handle.
Automatic Reconciliation, in contrast, is rule-based. It works extremely well when data is clean, structured, and predictable.
Many companies adopt a hybrid approach: Automatic Reconciliation for the bulk of transactions; Manual Reconciliation reserved for exceptions, unusual transactions, or compliance review. This hybrid use leverages speed and accuracy without sacrificing oversight or flexibility.
4. Cost Implications
The costs of reconciliation come from labor, time, risk, and opportunity cost. Manual Reconciliation often means more staff hours, higher headcount, overtime during busy periods, and slower reporting cycles.
Automatic Reconciliation demands upfront investment in software, integrations, and setup. But over time, the cost per transaction drops dramatically as volume increases, no need to hire more people. Automation also reduces costly errors, rework, audit issues, and time spent on backlog cleanup.
From a long-term perspective, especially for scaling businesses, Automatic Reconciliation often becomes more cost-effective than maintaining large manual teams, especially when transaction volume and complexity grow.
5. Audit, Compliance, and Reporting Readiness
One of the big benefits of Automatic Reconciliation lies in audit readiness and compliance. Automated systems generate timestamped logs, detailed audit trails, record who matched what and when, and produce standardized reconciliation reports.
Manual Reconciliation can support compliance too, but only if the team is extremely disciplined, consistent, and produces rigorous documentation. In many spreadsheet-based workflows, missing files, inconsistent naming conventions, or delayed updates weaken the audit trail.
Especially for multinational firms or businesses dealing with multiple currencies or intercompany accounts, automation offers a structural advantage for clean, reliable reporting.

Built for Fast, Automatic Reconciliation!

Simplifying Reconciliation and Expense Management with Bycard
The features and solutions that Bycard offers align strongly with the strengths of Automatic Reconciliation and hybrid finance operations:
- Receipt & expense tracking: link transactions to receipts, categories, and vendor info for faster audits.
- Multi-currency support: manage international vendor payments and ad campaigns easily.
- Spend control & budget limits: set per-card/project limits, lock/unlock cards, restrict merchants.
- Support for subscriptions, ad spend, and vendor payments: reduces manual payment tasks.
- Consolidated dashboards: monitor spend and reconciliation cycles in real time.
- Structured transaction data: enables accurate automatic matching and reduces manual reconciliation effort.
Which Reconciliation Method Fits Your Business Needs
| Reconciliation Type | When to Use / Key Points |
| Manual Reconciliation | Transactions requiring interpretation or additional validationPayout partners don’t provide enough metadata for automated matchingFrequent exceptions or manual adjustmentsInvestigating fraud, chargebacks, or anomaliesVerifying year-end balances or cleanup where accuracy outweighs speedCommon for early-stage businesses or small teams |
| Automatic Reconciliation | High-volume or rapidly growing transactionsSubscription businesses, marketplaces, or high-frequency paymentsSame-day or real-time reporting needsReduce repetitive manual tasksMulti-currency, multi-entity, or global operationsTeams focused on analysis and insights rather than data entry |
| Hybrid Approach | Automatic for standard, predictable, high-volume transactions, manual for exceptions, refunds, intercompany transfers, or complex cases. automated flags with manual review to resolve issues, periodic human audits for intercompany, FX, or complex invoice relationships, combines speed, accuracy, and context-aware judgment |
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Manual and Automatic Reconciliation helps you choose a process that fits your team and financial complexity. Manual Reconciliation offers control and context for transactions that need human judgment, while Automatic Reconciliation delivers speed, scale, and stronger audit readiness as volume grows. Most teams rely on a hybrid model, automation for routine matching and manual checks for exceptions. With tools like Bycard, this blended approach becomes both efficient and highly scalable.